Atlas of Obstetric Ultrasound
by The International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology
under the Editorship of Professor Gianluigi Pilu
Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Bologna, Italy
Contents:
•
•
•
o
o
o
o
o
o
•
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
•
o Color and pulsed Doppler of blood shunting across a muscular ventricular septal
Early pregnancy and embryogenesis
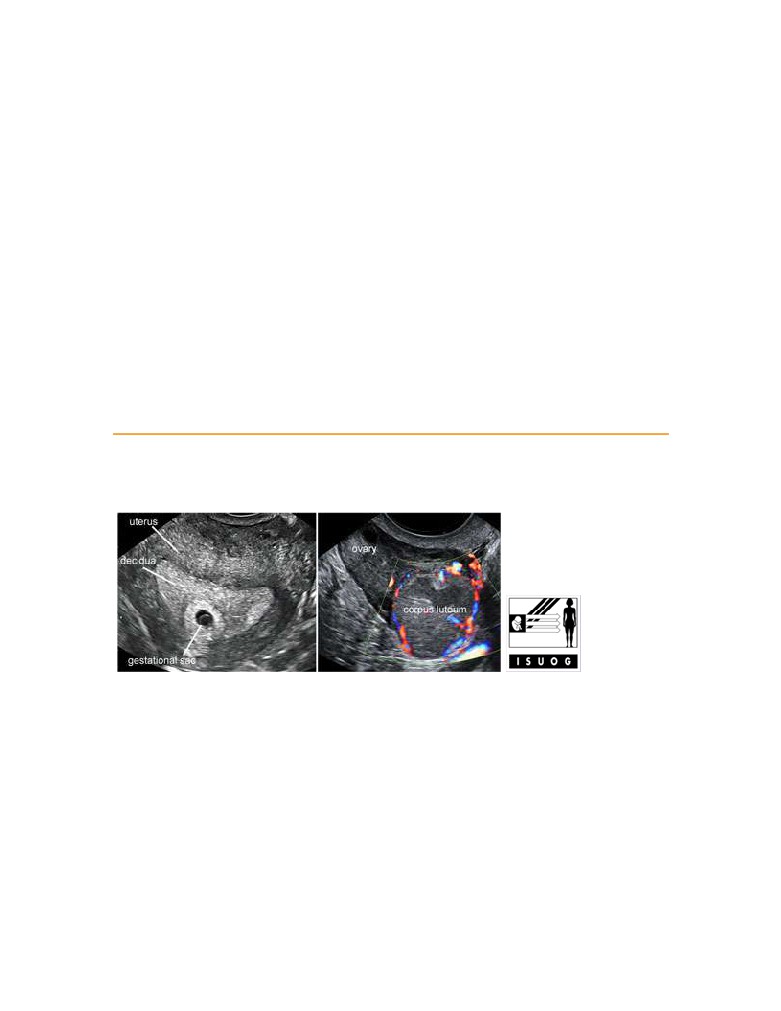
The gestational sac and the corpus luteum
Legend:The gestational sac and the corpus luteum
The corpus luteum
Legend:The corpus luteum
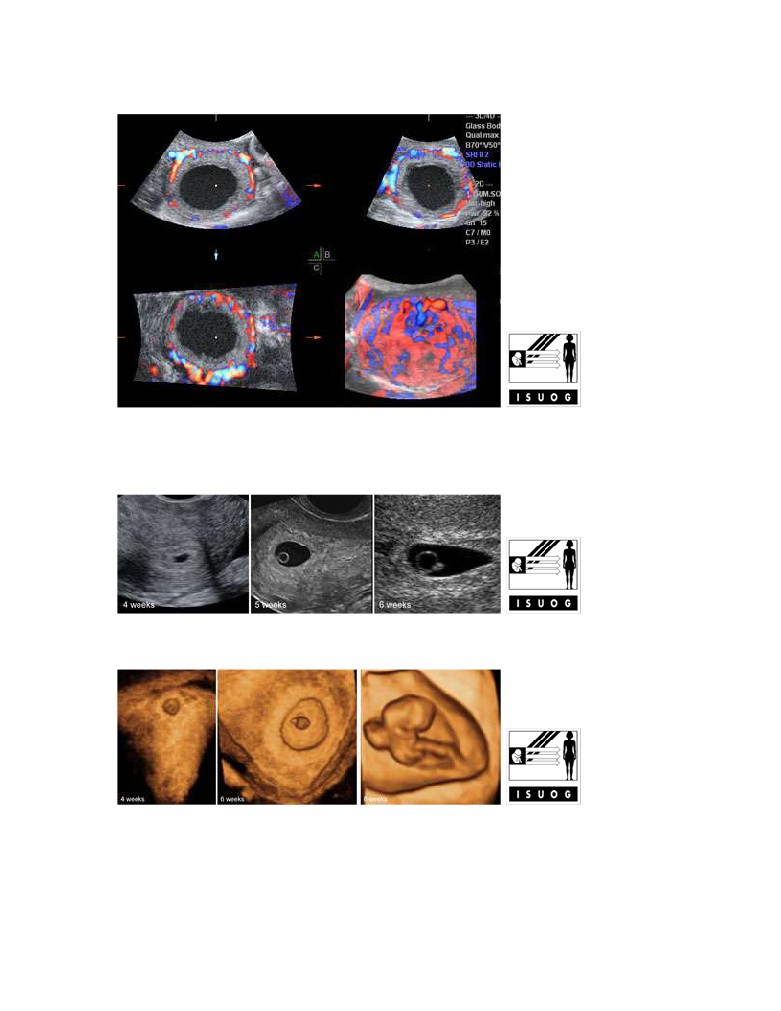
The gestational sac in 2D ultrasound at 4-6 weeks' gestation
Legend:The gestational sac in 2D ultrasound at 4-6 weeks' gestation
.The gestational sac in 3D ultrasound at 4-7 weeks' gestation
Legend:The gestational sac in 3D ultrasound at 4-7 weeks' gestation
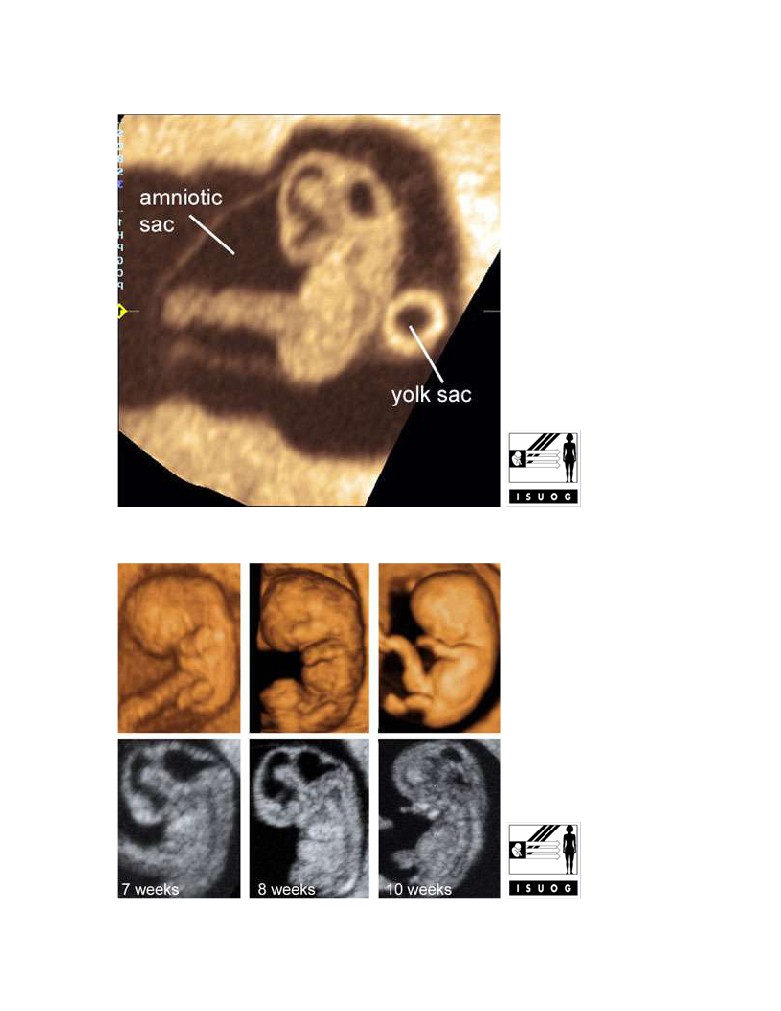
A close look at the gestational sac at 7 weeks' gestation
Legend:A close look at the gestational sac at 7 weeks' gestationEmbryo at 7-10
weeks' gestation
Legend:Sonography of the embryonic period with 3D (top) and 2D ultrasound. The
developing cerebral vesicles are well seen
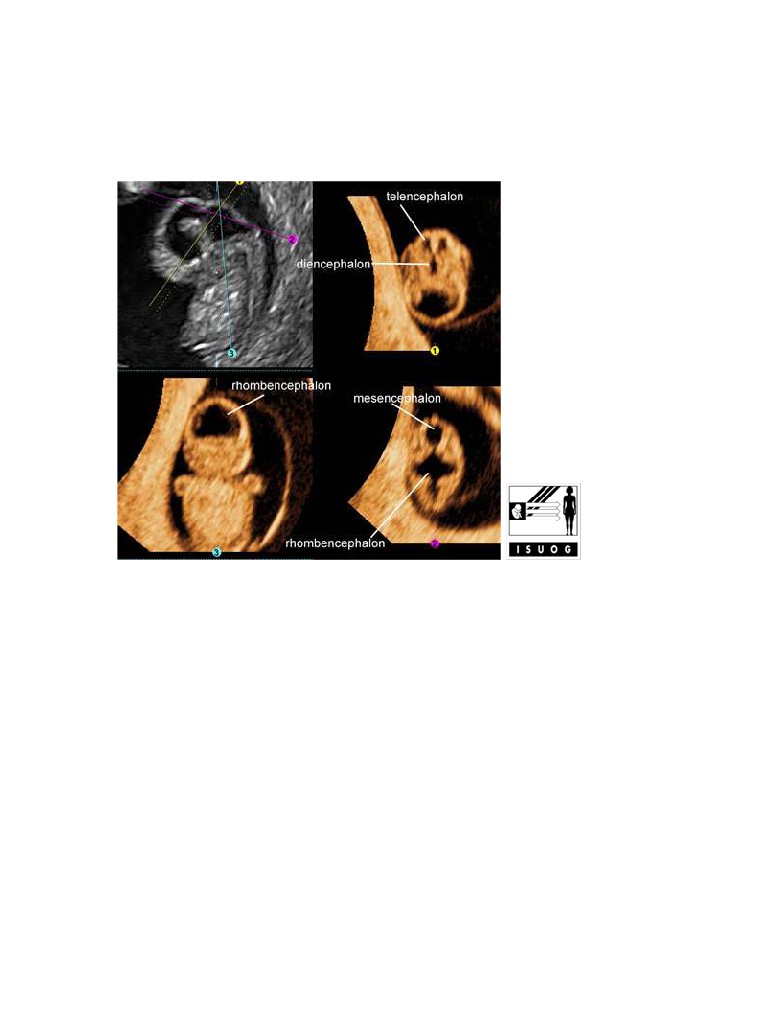
Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation
Legend:Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation
Reference(s):Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of
the forebrain and midbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from 7 to 12 weeks of
gestation.
Ultrasound
Obstet
Gynecol
1994;4(3):183-92.
PubMed
PMID: 12797178.Blaas HG, Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Hellevik LR. Early development of
the hindbrain: a longitudinal ultrasound study from
7 to
12 weeks of gestation.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(3):151-60. PubMed PMID: 7788488.Blaas HG,
Eik-Nes SH, Kiserud T, Berg S, Angelsen B, Olstad B. Three-dimensional imaging of
the brain cavities in human embryos. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1995;5(4):228-32.
Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation: the unfolded embryo
Legend:Brain vesicles at 8 weeks' gestation: the unfolded embryo
Casts of the cerebral vesicles at 7-10 weeks' gestation
Legend:Casts of the cerebral vesicles at 7-10 weeks' gestation
End of embryogenesis and beginning of fetal period: 11 weeks' gestation
Legend:End of embryogenesis and beginning of fetal period: 11 weeks' gestation
Fetal faces
Legend:Fetal faces
Reference(s):Rotten D, Levaillant JM. Two- and three-dimensional sonographic
assessment of the fetal face. 1. A systematic analysis of the normal face. Ultrasound
Obstet Gynecol 2004;23(3):224-31. PubMed PMID: 15027008.
Placenta
Normal placenta
Legend:Normal placenta
Normal umbilical cord
Legend:Normal umbilical cord
Placenta previa
Legend:Placenta previa
Placenta accreta
Legend:Placenta accreta
Velamentous insertion of the cord
Legend:Velamentous insertion of the cord
Reference(s):Sepulveda W, Rojas I, Robert JA, Schnapp C, Alcalde JL. Prenatal
detection of velamentous insertion of the umbilical cord: a prospective color Doppler
ultrasound study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003;21(6):564-9.
Vasa previa
Legend:Vasa previa
Chorioangioma of the placenta
Legend:Chorioangioma of the placenta
Molar pregnancy
Legend:Molar pregnancy
Single umbilical artery
Legend:Single umbilical artery
Umbilical cord cyst
Legend:Umbilical cord cyst
Cord hemangioma
Legend:Cord hemangioma
Abruptio placentae
Legend:Abruptio placentae
The fetal face
2D sonography of the fetal face
Legend:A combination of sagittal and coronal sections allows a detailed evaluation of
the fetal face from early gestation
3D sonography of fetal face
Legend:3D ultrasound is an ideal tool for the evaluation of the fetal face
The fetal palate
Legend:3D ultrasound allows the visualization of the fetal palate
3D ultrasound of the fetal skull
Legend:The bones that form the fetal skull and the interposed sutures and fontanelles
are visualized using an application of 3D ultrasound
Reference(s):Faro C, Benoit B, Wegrzyn P, Chaoui R, Nicolaides KH. Three-
dimensional sonographic description of the fetal frontal bones and metopic suture.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(6):618-21. PubMed PMID: 16193520.
3D tomography of fetal face
Legend:3D tomography of fetal face
Three-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of cleft palate: 'reverse face', 'flipped face' or
'oblique face'--which method is best? Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009;33(4):399-406.
PubMed PMID: 19109803.
Varieties of fetal facial clefts
Legend:Varieties of fetal facial clefts
Isolated cleft lip
Legend:Isolated cleft lip
Cleft lip and palate
Legend:Cleft lip and palate
Bilateral cleft lip and palate
Legend:Bilateral cleft lip and palate
Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
Legend:Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
Lateral cleft of the fetal face
Legend:Lateral cleft of the fetal face
Micrognathia
Legend:Micrognathia
Reference(s):Rotten D, Levaillant JM, Martinez H, Ducou le Pointe H, Vicaut E. The
fetal mandible: a 2D and 3D sonographic approach to the diagnosis of retrognathia
and micrognathia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol
2002;19(2):122-30. PubMed
PMID: 11876802.
Binder syndrome
Legend:Binder syndrome or maxillo-nasal dysplasia can be diagnosed in early
gestation. The prominent feature is the small nose with flattening of the fronto-nasal
angle. It is frequently associated with other anomalies affecting mostly the fetal
skeleton, malformations of the cervical spine, chondrodysplasia punctata and warfarin
embryopathy
Reference(s):Cook K, Prefumo F, Presti F, Homfray T, Campbell S. The prenatal
diagnosis of Binder syndrome before 24 weeks of gestation: case report. Ultrasound
Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(6):578-81. PubMed PMID: 11169356.
Apert syndrome
Legend:The combination of hypertelorism, a large metopic suture and finger
abnormalities is suggestive of Aper syndrome
Reference(s):Faro C, Chaoui R, Wegrzyn P, Levaillant JM, Benoit B, Nicolaides KH.
Metopic suture in fetuses with Apert syndrome at
22-27 weeks of gestation.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006;27(1):28-33. PubMed PMID: 16317802.
Trigonocephaly
Legend:An abnormal shape of the skull with a triangular forehead and a premature
closure of the metopic suture is suggestive of trigonocephaly, a rare form of
craniostenosis that is frequently associated with other anomalies
Reference(s):Chaoui R, Levaillant JM, Benoit B, Faro C, Wegrzyn P, Nicolaides KH.
Three-dimensional sonographic description of abnormal metopic suture in second-
and third-trimester fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005;26(7):761-4. PubMed
PMID: 16308900.
Skin tag
Legend:Skin tag
Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome
Legend:Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome is a rare congenital anomaly characterized
by overgrowth and different patterns of anomalies including mostly omphalocele,
macrosomia, macroglossia and placental dysplasia
The fetal brain
Normal fetal brain at midgestation: basic survey
Legend:Normal fetal brain at midgestation: basic survey
Reference(s):International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology
Education Committee. Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system:
guidelines for performing the 'basic examination' and the 'fetal neurosonogram'.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):109-16. PubMed PMID: 17200992.
Normal fetal brain at midgestation: advanced examination
Legend:Normal fetal brain at midgestation: advanced examination
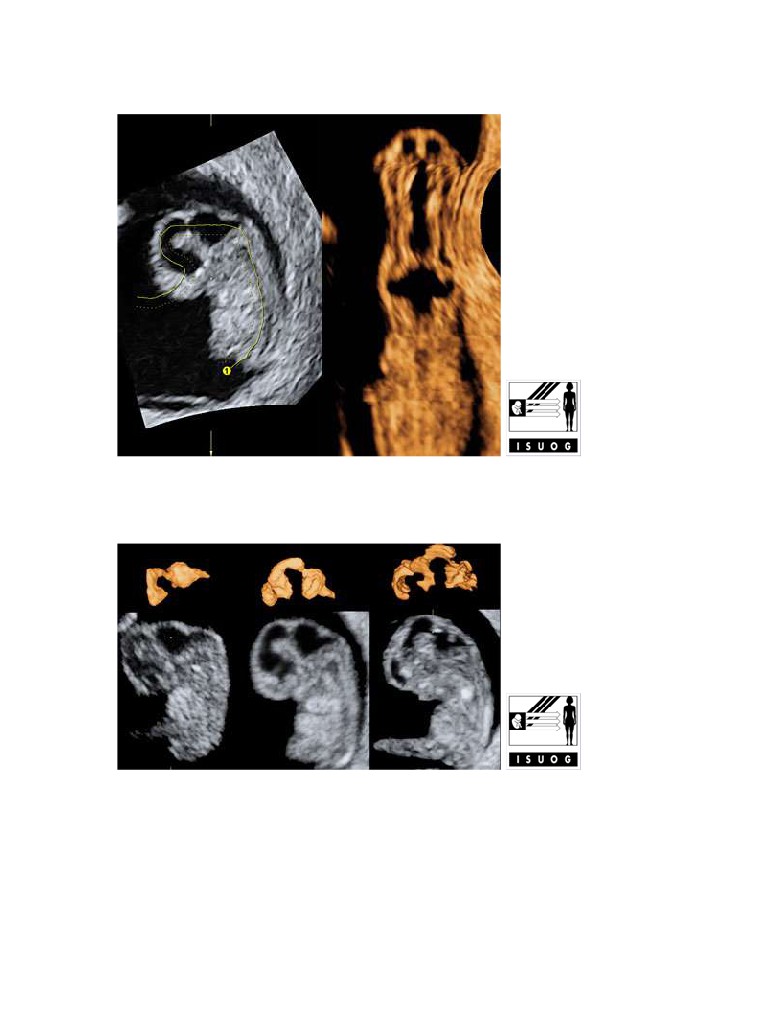
Fetal spine and neural canal
Legend:Fetal spine and neural canal
Reference(s):International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology
Education Committee. Sonographic examination of the fetal central nervous system:
guidelines for performing the 'basic examination' and the 'fetal neurosonogram'.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2007;29(1):109-16. PubMed PMID: 17200992.
Cerebral vessels
Legend:Cerebral vessels
Anencephaly throughout gestation
Legend:Anencephaly throughout gestation
Cephaloceles
Legend:Cephaloceles
Myelomeningocele
Legend:Myelomeningocele
Myelocele
Legend:Myelocele
Holoprosencephaly
Legend:Holoprosencephaly
Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
Legend:Facial anomalies with holoprosencephaly
Agenesis of the septum pellucidum
Legend:With agenesis of the septum pellucidum there is a central communication
between the cavities of the frontal horns
Complete agenesis of the corpus callosum
Legend:Complete agenesis of the corpus callosum: in most fetuses with complete
agenesis of the corpus callosum there is a wide interhemispheric fissure and lateral
separation of frontal horns
Partial agenesis of the corpus callosum
Legend:With partial agenesis of the corpus callosum only the most anterior portion is
present
Megacisterna magna
Legend:With megacisterna magna the depth of the cisterna magna is increased but
the cerebellum has a normal appearance and the fourth ventricle appears normally
closed by the posterior vermis
Dandy-Walker malformation
Legend:Dandy-Walker malformation is a distortion of the anatomy of the posterior
fossa characterized by the following elements: the cisterna magna is expanded and
the tentorium is displaced superiorly, the cerebellar vermis is rotated superiorly and
this results in a posterior opening of the fourth ventricle; the vermis may be normal,
hypoplastic or absent; the cerebellar hemispheres may be normal or hypoplastic;
ventriculomegaly and other anomalies are frequent
Blake’s pouch cyst
Legend:This anomaly is similar to the Dandy-Walker malformation but for the
tentorium that is in a normal position and the vermis that is by definition intact;
frequently it is a normal variant without clinical implications
Vermian hypoplasia
Legend:This anomaly is similar to Blake’s pouch cyst but for the hypoplasia of the
vermis that is small and dysmorphic. It was once referred to as ‘Dandy-Walker variant’
and is frequently associated with other anomalies
Cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
Legend:Cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
Types of cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
Legend:Types of cerebral lateral ventriculomegaly
Intracranial hemorrhage
Legend:A large blood clot within the distended lateral ventricles and a cystic cavity in
the periventricular cortex suggestive of a parenchymal infarction: this is a grade IV
hemorrhage
Porencephalic cyst
Legend:Porencephalic cyst
Schizencephaly: unilateral and bilateral
Legend:Schizencephaly: unilateral and bilateral
Periventricular leukomalacia
Legend:The cortex in the periventricular area appears inhomogeneous,
hyperechogenic with multiple microcysts
Brain findings with fetal cytomegalovirus infection
Legend:(a) and
(b) Periventricular echogenic halo similar to that described for
periventricular leukomalacia, mild ventriculomegaly, irregular choroid plexus; (c) a
more severe case; echogenicities within the cortex are associated with an excessive
size of the subarachnoid space suggesting microencephaly.
Brain findings with fetal toxoplasmosis
Legend:Mild ventriculomegaly, multiple echogenicities into the cortex
Intracranial arachnoid cysts
Legend:Intracranial arachnoid cysts
Choroid plexus cyst
Legend:Choroid plexus cyst
Vein of Galen aneurysm
Legend:Vein of Galen aneurysm
Lissencephaly
Legend:The surface of the brain is unusually smooth for a fetus at 28 weeks’
gestation (the Sylvian fossa is shallow and there is no sign of the cingulate and
precentral gyrus; the texture of the cortex is more irregular and echogenic than usual
Unilateral megalencephaly
Legend:Overgrowth of one hemisphere that appears brightly echogenic with a lateral
ventricle irregularly enlarged
Intracranial tumors
Legend:Teratoma results in complex masses that cannot be clearly differentiated from
the surrounding normal brain tissue; craniopharyngioma is a well defined echogenic
mass.
The fetal heart
Normal fetus situs
Legend:Normal fetus situs
Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of fetal cardiac connections
Legend:Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of fetal cardiac connections
Color Doppler of fetal cardiac connections
Legend:Color Doppler of fetal cardiac connections
The fetal aortic arch
Legend:The fetal aortic arch
High definition flow of the fetal aortic arch
Legend:High definition flow of the fetal aortic arch
Color Doppler of pulmonary veins
Legend:Color Doppler of pulmonary veins
Three-dimensional ultrasound of normal fetal heart
Legend:Three-dimensional ultrasound of normal fetal heart
Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of ventricular septal defects
Legend:Two-dimensional gray scale imaging of ventricular septal defects
Color and pulsed Doppler of blood shunting across a muscular ventricular septal
defect
Legend:Color and pulsed Doppler of blood shunting across a muscular ventricular
septal defect
Muscular ventricular septal defect
Legend:Muscular ventricular septal defect
Inlet ventricular septal defect
Legend:Inlet ventricular septal defect
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C.
Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118-22. PubMed PMID: 11117079.
Outlet ventricular septal defect
Legend:Outlet ventricular septal defect: the arrow indicates a large defect of the outlet
portion of the ventricular septum associated with malalignment of the great vessels
Reference(s):Paladini D, Palmieri S, Lamberti A, Teodoro A, Martinelli P, Nappi C.
Characterization and natural history of ventricular septal defects in the fetus.
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2000;16(2):118-22. PubMed PMID: 11117079.
Perimembranous ventricular septal defect
Legend:Perimembranous ventricular septal defect
Apical ventricular septal defect
Legend:Apical ventricular septal defect
Complete atrioventricular canal
Legend:Complete atrioventricular canal
Partial atrioventricular canal
Legend:Partial atrioventricular canal: two separate atrioventricular valves insert at the
same level on the ventricular septum, and there is a defect of the atrial septum primum
Single ventricles
Legend:Types of single ventricles: atresia of the tricuspid valve and double inlet single
ventricle
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Legend:Hypoplastic left heart syndrome: there is a small left ventricle with an internal
echogenic lining suggestive of endocardial fibroelastosis, there is no flow across the
mitral valve and the aortic arch is perfused in a retrograde manner
Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum
Legend:Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum: the right ventricle is small,
there is significant tricuspid regurgitation, there is no flow across the pulmonary vale,
and there is streaming of flow into the pulmonary artery as a consequence of
retrograde perfusion through the ductus arteriosus
Ebstein malformation of the tricuspid valve
Legend:Ebstein malformation of the tricuspid valve: the leaflets of the tricuspid valve
are displaced apically compared to the atrioventricular junction and there is massive
tricuspid regurgitation
Tricuspid dysplasia
Legend:Cardiomegaly, enlargement of the right side of the heart and right atrium in
particular, massive regurgitation across a normally inserted tricuspid valve
Tetralogy of Fallot
Legend:Tetralogy of Fallot: a large aorta overrides the ventricular septum, the
pulmonary artery patent but significantly reduced in size and the right outflow tract is
restricted
Complete transposition of great arteries
Legend:Complete transposition of great arteries: two great vessels arise in parallel
fashion from the base of the heart without crossing; the posterior vessel connected to
the left ventricle bifurcates and can therefore be positively identified as the pulmonary
artery; the anterior vessel arising from the right ventricle has a long upward course
and is the aortic arch
Double outlet right ventricle
Legend:Double outlet right ventricle: there is large outlet septal defect and the two
great arteries arise side by side predominantly from the right ventricle
Truncus arteriosus communis
Legend:Truncus arteriosus communis: a single large vessel with a thickened valve
arises from the base the heart and give rise to the aortic arch and main pulmonary
artery
Reference(s):Paladini D, Rustico M, Todros T, Palmieri S, Gaglioti P, Benettoni A,
Russo MG, Chiappa E, D'Ottavio G. Conotruncal anomalies in prenatal life. Ultrasound
Obstet Gynecol 1996;8(4):241-6. PubMed PMID: 8916376.
Interrupted aortic arch
Legend:Interrupted aortic arch: there is ventricular disproportion and the ascending
aorta is not connected to the descending portion
Coarctation/tubular hypoplasia of aortic arch
Legend:Coarctation/tubular hypoplasia of aortic arch: ventricular disproportion with
dominance of the right cavities, small aortic arch compared to the ductal arch in the
transverse view, small and tortuous aortic with the impression of a shelf in the
longitudinal views
Aortic stenosis
Legend:Aortic stenosis: hypertrophic left ventricle, thickened aortic valve, slightly
enlarged aortic root with high velocity turbulent flow and mitral regurgitation
Pulmonic stenosis
Legend:Pulmonic stenosis: severe hypertrophy of right ventricle with little anterograde
flow and regurgitation across the tricuspid valve; thickened and poorly opening
pulmonary valve; streaming of flow into the pulmonary artery due to the combination of
anterograde high velocity flow across the stenotic pulmonic valve and retrograde flow
from the ductus venosus
Cardiac anomalies associated with isomerism
Legend:Cardiac anomalies associated with isomerism: common atrium
(CA),
atrioventricular canal (AV canal) with abnormal connections of the pulmonary veins,
parallel great vessels
Left isomerism
Legend:Left isomerism: interruption of the inferior vena cava with azygos continuation
Right isomerism
Legend:Right isomerism: abnormal disposition of abdominal organs; the inferior vena
cava is present
Liver in isomerism
Legend:Liver in isomerism